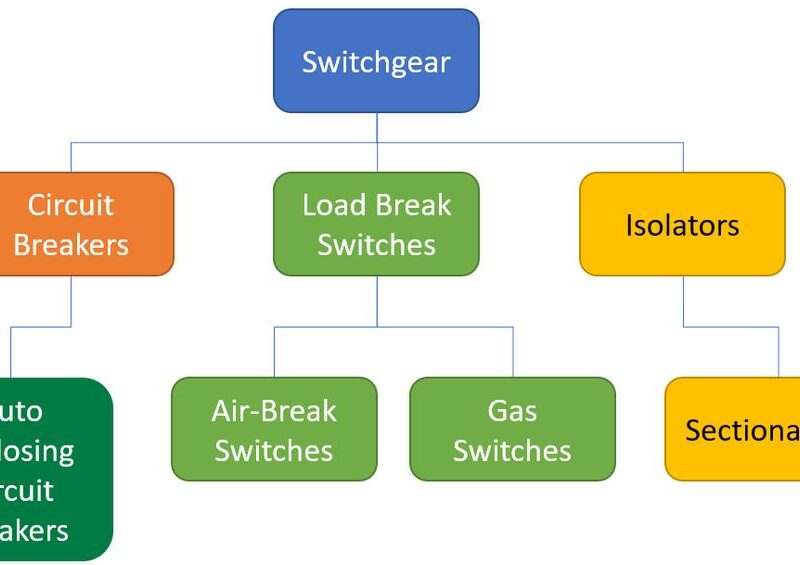
An Overview of Switchgear Classification
For those new to the electrical industry, understanding switchgear and its various classifications can be challenging. While engineering curricula cover switchgear concepts, there is often a gap between academic learning and real-world industry applications. Drawing from my experience, I’d like to provide a concise overview of switchgear and its classifications to bridge this gap.
What is Switchgear?
Switchgear refers to equipment designed to carry, make, and break electrical currents under normal and abnormal conditions. It isolates faulty sections of the electrical system to protect both human life and property from potential damage.
Classification of Switchgear
Switchgear can be categorized based on several criteria, including voltage class, installation type, insulation medium, and network position.
1. Voltage Classification
Switchgear is broadly classified into three categories based on voltage levels:
- Low Voltage (LV) Switchgear: Operates below 1 kV and is commonly used in power electronics circuits. Examples include switch fuse units, high rupturing capacity (HRC) fuses, air circuit breakers (ACB), miniature circuit breakers (MCB), and molded case circuit breakers (MCCB).
- Medium Voltage (MV) Switchgear: Covers voltage levels from 1 kV to 33 kV. Common types include bulk oil circuit breakers (BOCB), minimum oil circuit breakers (MOCB), sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) circuit breakers, vacuum circuit breakers (VCB), and SF6-free circuit breakers.
- High Voltage (HV) Switchgear: Ranges from 33 kV to 220 kV, with further classifications:
- Extra High Voltage (EHV): 220 kV to 760 kV
- Ultra High Voltage (UHV): Above 800 kV
2. Installation Type
Switchgear can be categorized based on where it is installed:
- Indoor Switchgear: Enclosed within a controlled environment, with ingress protection (IP) ratings ranging from IP1X to IP6X. These are further classified as:
- Metal-enclosed switchgear: Fully enclosed with metal sheets housing primary interrupting devices and fuses.
- Metal-clad switchgear: Compartmentalized design with separate compartments for circuit breakers, relays, and meters, providing enhanced safety.
- Examples: Indoor isolators, VCBs, ring main units (RMU).
Advantages: Reliable, compact, low maintenance, and less affected by environmental factors.
Limitations: Higher initial cost. - Outdoor Switchgear: Designed for open-air installations with protection against environmental factors such as rain and dust. Commonly used for HV, EHV, and UHV applications.
- Examples: Porcelain-clad VCBs, outdoor isolators, RMUs, compact secondary substations (CSS).
Advantages: Suitable for large-scale power distribution.
Limitations: Bulky, requires more space and maintenance.
3. Insulation Medium
The insulating medium in switchgear prevents unintended arcing and determines the switchgear’s size and performance.
- Air-Insulated Switchgear (AIS): Uses natural air as the insulating medium. While cost-effective, it requires a larger physical footprint due to air’s lower dielectric strength.
- Oil-Insulated Switchgear: Uses insulating oil, providing better dielectric strength and cooling properties but requiring regular maintenance.
- Solid-Insulated Switchgear: Encased in epoxy insulation, making it compact and environmentally friendly. However, defects in manufacturing can impact reliability.
- Gas-Insulated Switchgear (GIS): Uses pressurized SF6 gas for superior insulation and compact design. However, SF6 has significant environmental concerns.
- SF6-Free Switchgear (Climate-Friendly Dry Air Insulation): Uses dry air as an alternative to SF6, offering the benefits of GIS while being environmentally friendly.
Example: Nuventura’s NU1 is an IEC-certified, SF6-free medium voltage (up to 36 kV) GIS for primary distribution.
4. Network Position
Switchgear can also be classified based on its placement in the power distribution network:
- Primary Switchgear: Handles higher fault currents (typically above 20 kA) and is used near high-voltage transformers for full voltage and current protection. Circuit breakers are the primary interrupting devices.
- Example: Nuventura’s NU1, a 36 kV SF6-free GIS for primary distribution.
- Secondary Switchgear: Operates at lower fault currents (below 20 kA) and normal currents (below 630 A), typically located near low-voltage transformers. Main interrupting devices include fuses, load break switches, and circuit breakers.
Conclusion
Understanding the classifications of switchgear is essential for selecting the right equipment for various applications. As industry standards evolve, transitioning to sustainable, SF6-free alternatives will be crucial for minimizing environmental impact.
Professiona Switchgear supplier and manufacturer
- Zhejiang GONGSHUN Electrical Co.,Ltd (electricgs.com), Our company was founded in the late 1990s, specializing in the production of inflatable cabinets, SF6 inflatable cabinets, and various high and low voltage complete sets of electrical equipment. It has multiple subsidiaries under its jurisdiction, including high-voltage load switch branch, high-voltage circuit breaker branch, high-voltage fuse branch, and technology development branch.Our technical expertise, comprehensive product portfolio and long-term rich experience are helping many customers in need to solve their power problems. We’re happy to help at any time. Whether you need application product advice or technical assistance, our global service team is committed to providing you with the right support. For more technical information about medium voltage earthing switch, feel free to contact us, send an email to gongshun@electric-cn.com
- Our company specializes in producing 12KV-40.5KV series high-voltage electrical products: FZN58, FLN48, FLN36, FZRN25, FZN21, FN18, ZFN16, FN12, FN8, FN7, FN5, XRNT, XRNP, VS1, ZN28, ZW8, ZW32, JN15, GN19, GN22, GN24, GN30, CLXGN15-12, HXGN □ -12, DXG-12 (L), DFW □ -12 high-voltage cable branch box, CLXGN □ -12 (SF6) series inflatable cabinet 12KV and 35KV cable accessories, etc; CLVXP-12 indoor AC high voltage fixed switchgear, CL-SIS-12 compact solid insulated ring main unit, professional assembly Schneider SC6 (SF6) series load switchgear, ABB produced SFG (SF6) series load switchgear and other series products; Distribution and agency of high-voltage load switches and inflatable cabinets produced by Schneider Electric and ABB; Siemens produces the 3AJ1 series of indoor medium voltage vacuum circuit breakers and other related products. The company has a complete range of products and has been operating safely on domestic and international power grids for a long time, receiving unanimous praise from both new and old users. Among them, multiple products such as FZRN25, FN12, FLN36-12, XRNT-12 have been exported to various countries and regions in East Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, and the United States.
