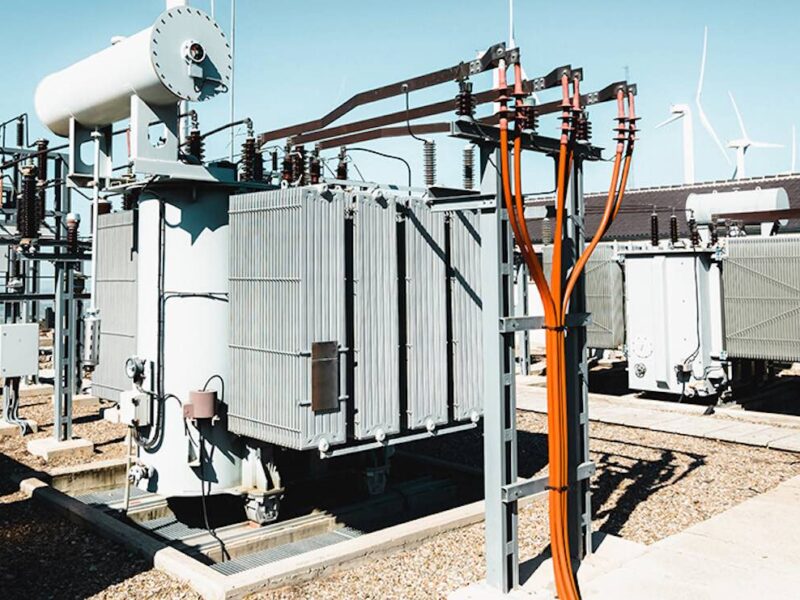

Oil Immersed Transformer: Structure, Working Principle, Types, and Considerations
Power transformers are the most critical components in electrical power systems. The design of grid transformers varies depending on the cooling and electrical insulation systems used. Transformers are typically categorized into dry-type and oil-immersed types. Currently, most transformers in use are oil-immersed. These are also referred to as oil-immersed transformers.
Oil-immersed transformers use oil as an insulation and cooling medium, offering advantages such as reasonable structure, excellent performance, cost-effectiveness, and low noise. They are well-suited for urban, rural, and industrial power grid modifications, combined transformers, and pre-installed substation transformers. Compared to dry-type transformers, the use of liquid cooling provides better heat dissipation, enabling higher rated power and greater efficiency.
This article will introduce the structure, working principle, common types, and precautions for oil-immersed transformers.
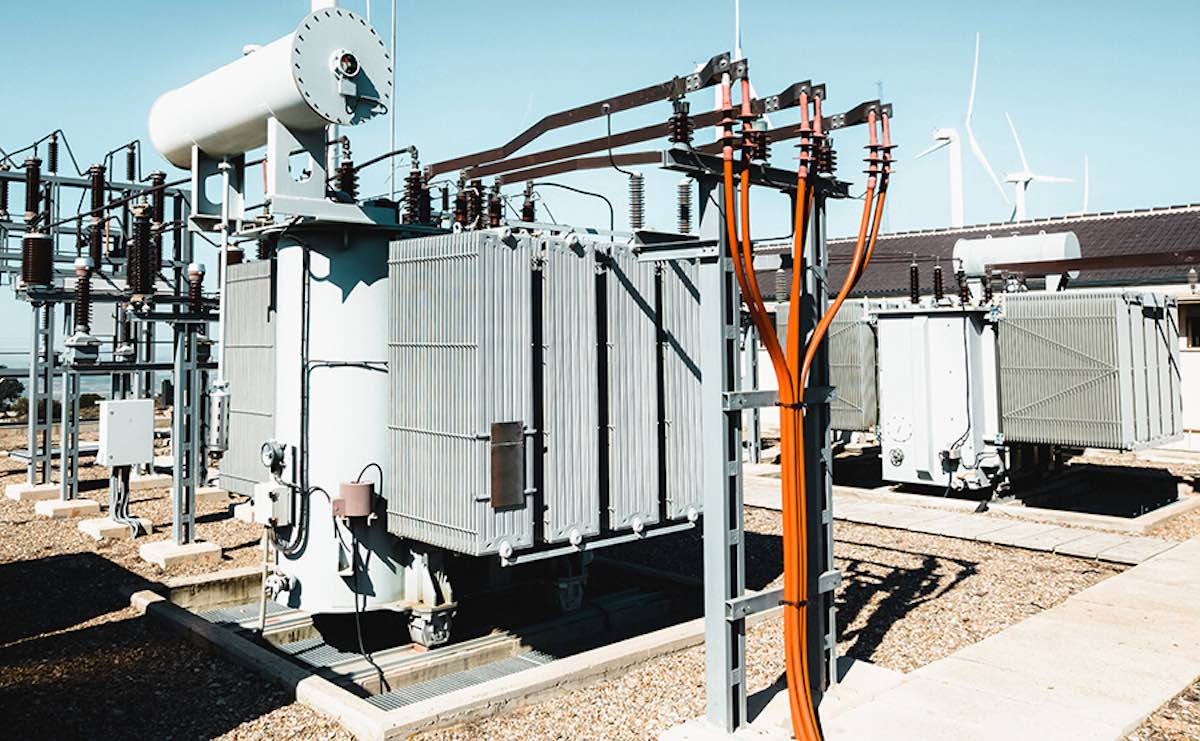

1. What is an Oil-Immersed Transformer?
An oil-immersed transformer is a common type of electrical transformer that uses insulating oil to cool and insulate the internal components of the transformer.
It consists of two or more coils (primary and secondary windings) and a core. The main body is sealed in a welded steel oil tank filled with insulating oil. During operation, the heat generated by the coils and the core is first transferred to the insulating oil, which then circulates and cools the transformer. The coils and the core are submerged in the insulating oil to maintain their cooling and insulation properties.
2. Working Principle of an Oil-Immersed Transformer
The working principle of an oil-immersed transformer is based on electromagnetic induction. Its key components include the core, windings, and bushings. The core is responsible for the flow of magnetic flux, while the windings, made of conductor coils wound on the core, generate a magnetic field. The windings are insulated with layers of cardboard and shields, and their thickness increases with higher voltage. Bushings connect the transformer windings to the substation.
These transformers are used in distribution and substation systems, where the core and windings are immersed in oil for cooling and insulation. The oil circulates inside the core and winding components through convection. Cooling methods vary; transformers with smaller rated power rely on external cooling, while larger transformers use air-cooled radiators.
Oil-immersed transformers require insulating oil to operate. The oil serves two purposes: it cools the internal components, maintaining safe operating temperatures, and it provides electrical insulation, preventing arcing and discharge.
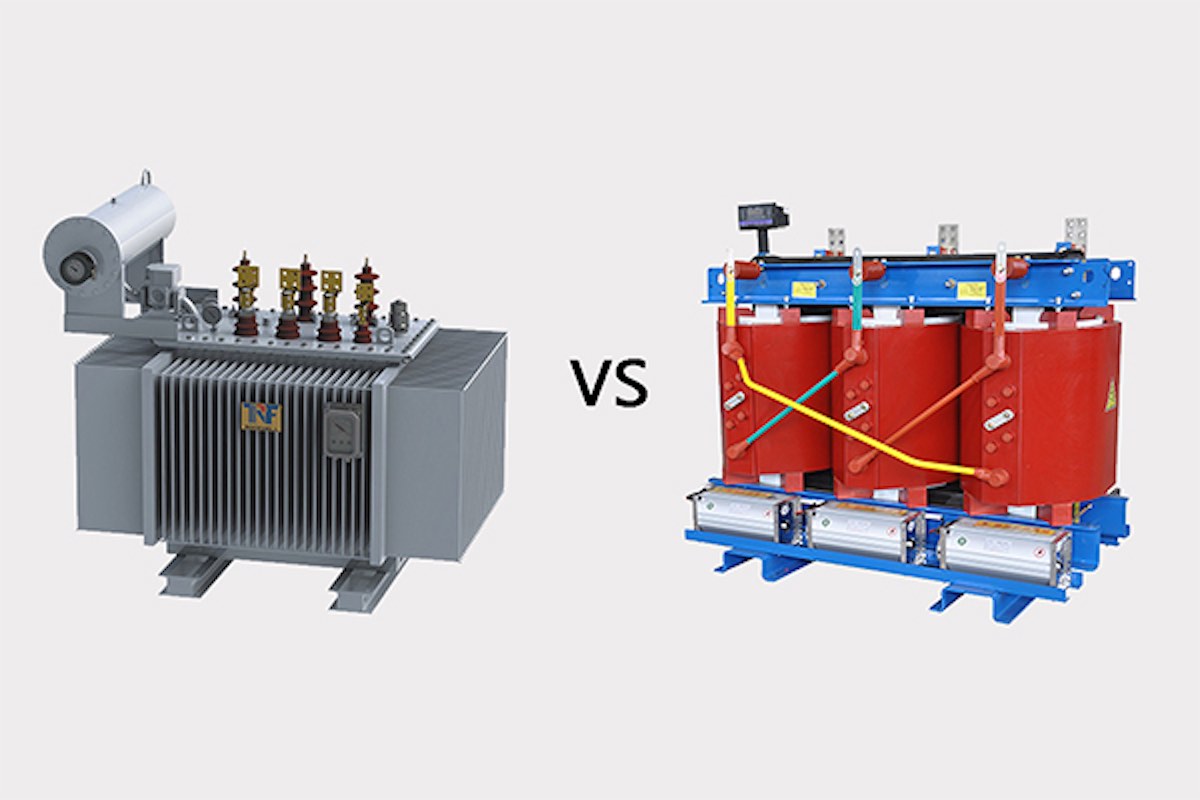
3. Oil-Immersed Transformer vs Dry-Type Transformer
Oil-immersed transformers have the coils and core submerged in specialized transformer oil. The advantage of this is that it isolates the cooling coils from the air, preventing moisture in the air from corroding the core and helps extinguish electrical arcs. Therefore, early electrical transformers and power switches were all immersed in oil.
Dry-type transformers are fixed with the core and windings integrated, and they can be exposed to the air or placed indoors. These require more stringent environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity control. Dry-type transformers can operate unattended with periodic checks.
Dry-type transformers use air as the cooling medium, while oil-immersed transformers use oil, which offers better cooling performance and higher voltage tolerance.
4. Advantages of Oil-Immersed Transformers
Oil-immersed transformers are cheaper compared to dry-type transformers, with the same capacity typically costing half the price of a dry-type transformer.
The cooling efficiency of oil-immersed transformers is generally better than dry-type transformers, as oil is a better cooling medium. Oil-immersed transformers also have a higher voltage tolerance. While dry-type transformers can handle up to 35 kV, oil-immersed transformers are not limited by this threshold. Furthermore, oil-immersed transformers are more versatile.
Oil-immersed transformers are more environmentally friendly as they are easier to recycle. They are more compact and perform better in outdoor environments, especially to prevent oil leakage or other accidents.
5. Types of Oil-Immersed Transformers
There are many types of oil-immersed transformers, including:
- Single-phase transformers: Used in rural areas or low-load environments.
- Three-phase transformers: Consist of windings on a core divided into three parts. They are used in high-load areas and can supply power to three circuits.
- Power transformers: Designed to handle higher loads. They step up or step down voltage and transmit power from one place to another.
- Distribution transformers: Deliver lower voltage from the grid to homes and businesses. They are much smaller than power transformers.
- Pole-mounted transformers: Installed on utility poles.
- Pad-mounted transformers: Installed on a concrete foundation on the ground.
6. Insulating Oil for Oil-Immersed Transformers
Oil-immersed transformers require special oil, known as transformer oil or insulating oil. The quality of the oil significantly affects the transformer’s lifespan and safety.
Transformer oil differs from other oils in several aspects:
- Dielectric strength: Transformer oil has a high dielectric strength, preventing leaks. This is crucial because oil-immersed transformers must withstand high voltage.
- Quality: Transformer oil is chemically stable and heat-resistant, preventing degradation over time.
- Viscosity: The viscosity of transformer oil is closely monitored, as low viscosity oil can cause poor heat transfer, while high viscosity oil increases power loss.
- Purification: To avoid transformer damage and maintain insulation properties, the oil must be thoroughly cleaned.
When an oil-immersed transformer requires replenishing insulating oil, ensure the oil is of the same brand and specification as the original. Different types of oil should not be mixed or interchanged.
7. Selecting an Oil-Immersed Transformer
Oil-immersed transformers come in various types and are widely used. Before selecting the right type, consider the following factors:
- Load type and power: The rated capacity of the transformer should be based on the load type and power. If the load involves peak loads (e.g., motors or inverters), a transformer with higher overload capacity is needed.
- Input and output voltage: Choose the appropriate transformer model based on input and output voltage requirements.
- Environmental conditions: Transformers should be placed in well-ventilated, dry, dust-free, and non-corrosive environments to avoid the effects of water, humidity, and dust. Select transformers with special requirements such as anti-corrosion, anti-moisture, and explosion-proof designs.
- Lifespan and maintenance cost: Consider the transformer’s expected lifespan and maintenance costs. Typically, well-known brands with mature technology and easy maintenance are more reliable.
- Safety performance: Choose transformers with good safety features such as overload and short-circuit protection to ensure equipment and personnel safety.
- Price: Select a suitable product based on your budget. In addition to the price, consider product quality and reliability.
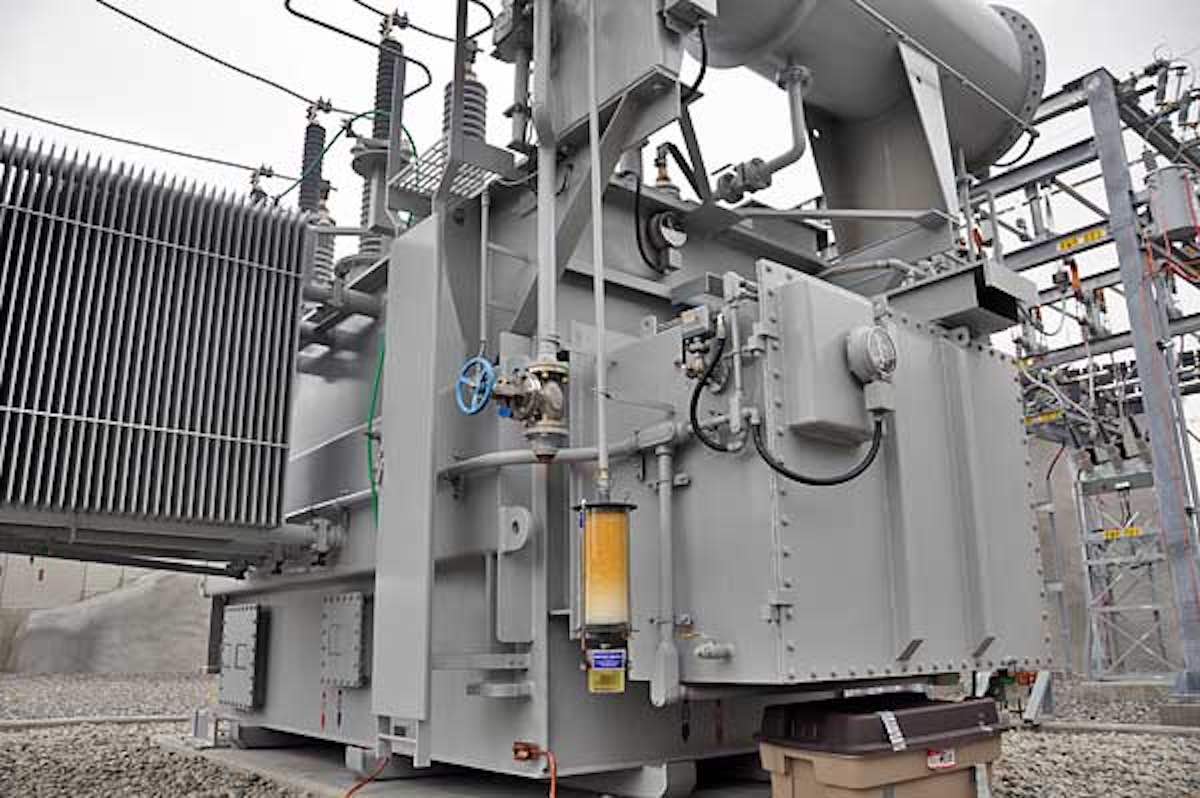

8. Maintenance and Precautions for Oil-Immersed Transformers
The building housing the transformer must meet fire-resistance standards. In the event of a fire, measures should be taken to prevent oil leakage and the spread of fire, while ensuring the fire is extinguished.
To ensure normal operation, transformers must be regularly inspected and maintained. This includes checking for any leaks, cleaning the transformer’s internal and external components, and ensuring safe operation. Otherwise, malfunctions may occur, posing serious risks.
If oil leakage occurs, the transformer should be shut down immediately for repairs. Oil leakage can disrupt the monitoring system and the accuracy of oil level indicators. A sealed transformer that loses its sealing integrity is vulnerable to moisture intrusion, leading to insulation degradation, affecting the transformer’s safe and reliable operation.
Additionally, waste oil can easily pollute the environment, so proper disposal of this waste is crucial.
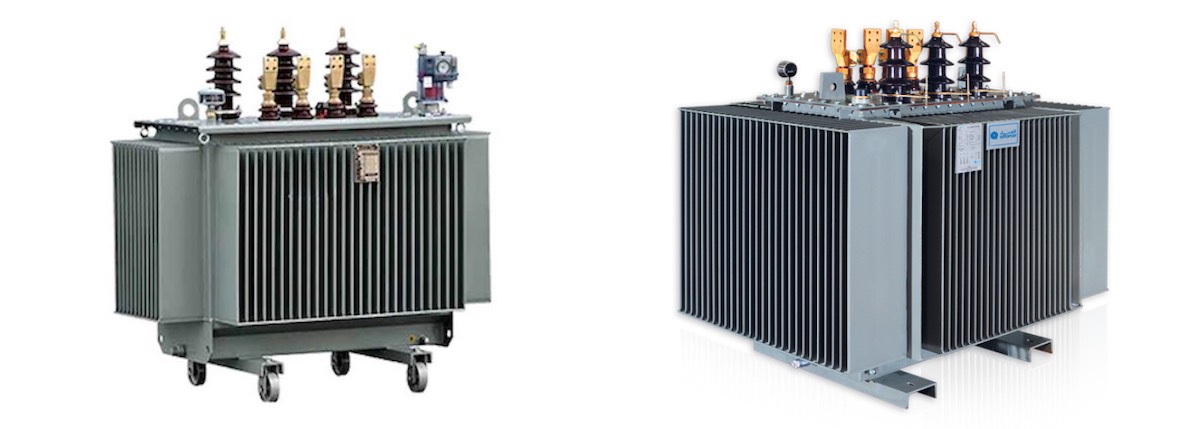

9. Conclusion
Oil-immersed transformers have many advantages and are generally superior to dry-type transformers. They are efficient, cost-effective, and suitable for almost any capacity. While oil-immersed transformers require maintenance and carry some safety risks, proper care and usage can maximize their performance.
Professiona Switchgear supplier and manufacturer
- Zhejiang GONGSHUN Electrical Co.,Ltd (electricgs.com), Our company was founded in the late 1990s, specializing in the production of inflatable cabinets, SF6 inflatable cabinets, and various high and low voltage complete sets of electrical equipment. It has multiple subsidiaries under its jurisdiction, including high-voltage load switch branch, high-voltage circuit breaker branch, high-voltage fuse branch, and technology development branch.Our technical expertise, comprehensive product portfolio and long-term rich experience are helping many customers in need to solve their power problems. We’re happy to help at any time. Whether you need application product advice or technical assistance, our global service team is committed to providing you with the right support. For more technical information about medium voltage earthing switch, feel free to contact us, send an email to gongshun@electric-cn.com
- Our company specializes in producing 12KV-40.5KV series high-voltage electrical products: FZN58, FLN48, FLN36, FZRN25, FZN21, FN18, ZFN16, FN12, FN8, FN7, FN5, XRNT, XRNP, VS1, ZN28, ZW8, ZW32, JN15, GN19, GN22, GN24, GN30, CLXGN15-12, HXGN □ -12, DXG-12 (L), DFW □ -12 high-voltage cable branch box, CLXGN □ -12 (SF6) series inflatable cabinet 12KV and 35KV cable accessories, etc; CLVXP-12 indoor AC high voltage fixed switchgear, CL-SIS-12 compact solid insulated ring main unit, professional assembly Schneider SC6 (SF6) series load switchgear, ABB produced SFG (SF6) series load switchgear and other series products; Distribution and agency of high-voltage load switches and inflatable cabinets produced by Schneider Electric and ABB; Siemens produces the 3AJ1 series of indoor medium voltage vacuum circuit breakers and other related products. The company has a complete range of products and has been operating safely on domestic and international power grids for a long time, receiving unanimous praise from both new and old users. Among them, multiple products such as FZRN25, FN12, FLN36-12, XRNT-12 have been exported to various countries and regions in East Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, and the United States.
